
Harmonics can limit the dynamic performance of a converter. Harmonics are noise components related to, or generated by, a-d conversion. The ratio of the rms sum of the first six harmonics to the amplitude of the fundamental frequency.
The ratio of the fundamental frequency's amplitude to that of the largest spurious signal in a given bandwidth. INL produces additional harmonics and spurs in the frequency domain. The difference between the ideal and actual output when the converter input is at full scale. Gain error/full-scale error, expressed in terms of LSB The difference between the ideal and actual output when the converter input is zero.Ĭalculated after offset and gain errors are removed. The narrowing or widening of code widths caused by DNL can lead to “missing codes” and add noise and frequency spurs beyond the effects of quantization. The deviation of an actual code transition point from its ideal position on a straight line drawn between the end points of the transfer function. Integral nonlinearity (INL), expressed in terms of LSB
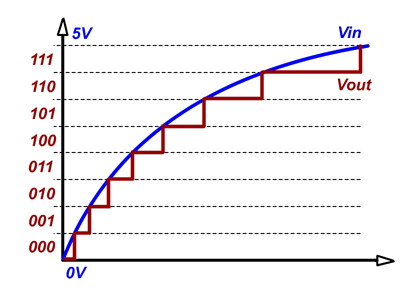
In an ideal converter, every code is exactly the same size and DNL is zero.ĭNL, INL, offset error, and gain error specify how accurately the data represents the signal across the entire internal and external range. The deviation from the ideal (1 LSB) code width between any two adjacent codes. LSB size is a function of converter resolution.ĭifferential nonlinearity (DNL), expressed in terms of LSB The right-most bit in an ADC output code. The number of repetitive conversions per second for a full-scale change to specified resolution and linearityĭetermines the fastest sampling capability of the ADC Number of bits representing an analog signal, generally ranging from 6 to 24.ĭetermines how small an input can be resolved.Ĭonversion speed or rate, ksamples/s or Msamples/s Specification and terms, units of measure


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
